
The majority of reported cases of gonorrhea occur in people under the age of 30. All people who are sexually active, including people who experience sexual violence, may be at risk for gonorrhea. A notifiable disease must be reported to public health authorities when an infection is confirmed by a clinic, doctor or laboratory. Gonorrhea is the second most common notifiable STI in Canada. Gonorrhea can be passed during childbirth if the newborn has come into contact with infected vaginal discharge or fluid.¹ ,² ,³ ,⁴ Who is at risk? It is theoretically possible to transmit gonorrhea through a hand job or fingering if infected fluids are present. Shared sex toys can also transmit gonorrhea. Oral-anal contact (rimming) can transmit gonorrhea as well.
Gonorrhea can be transmitted when a person who has the infection in their mouth or throat performs oral sex on another person or when a person performs oral sex on a person who has a genital infection. Transmission occurs when secretions from infected mucous membranes or semen of a person with a urethral infection come into contact with the mucous membranes of another person.Ĭondomless penetrative vaginal sex and anal sex are the highest-risk behaviours for the transmission of gonorrhea. Gonorrhea can be transmitted through sexual contact and sharing of sex toys. In addition, it can also infect the eyes through contact with infected discharge.¹ ,² How is gonorrhea transmitted? It can also infect the mouth, throat (pharynx), anus and rectum. Gonorrhea can infect the genital tracts, including the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, urethra (the tube that allows urine and semen to pass out of the body) and epididymis (a tube in the testicle that stores and carries sperm). The bacterium infects the “wet” linings (mucous membranes) of the body. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Key messages on gonorrhea for clients are available here. CATIE acknowledges and respects that people use words that they are most comfortable with. Some transgender ii people may use other terms, such as front hole and strapless. Cisgender i people can often identify with these terms. This text uses medical terms, such as vagina and penis, to describe genitals. People use different terms to describe their genitals. The words we use here – CATIE is committed to using language that is relevant to everyone. Gonorrhea can increase the risk of sexual transmission of HIV.Ĭorrect and consistent condom use reduces the risk of gonorrhea transmission. Gonorrhea can be treated and cured using antibiotics, although some strains of gonorrhea have become resistant to some antibiotics.
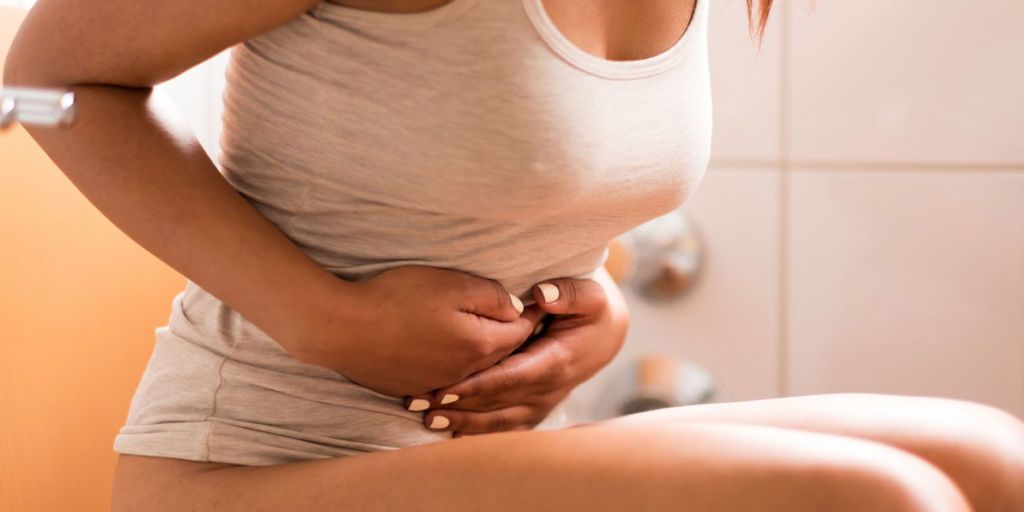

To test for gonorrhea, samples are taken from the sites of suspected infection and tested for the presence of the bacteria. Symptoms can include vaginal pain, painful urination, and an abnormal discharge from the vagina, urethra or rectum. If symptoms do occur, they usually appear one to seven days after infection.

Many people with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. Gonorrhea can infect the urethra (the tube that allows urine and semen to pass out of the body), cervix, rectum, throat, mouth and eyes. All people who are sexually active may be at risk for gonorrhea. It can be transmitted through sexual contact. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by a bacterium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
